nginx顶层模块读取配置的流程如下:
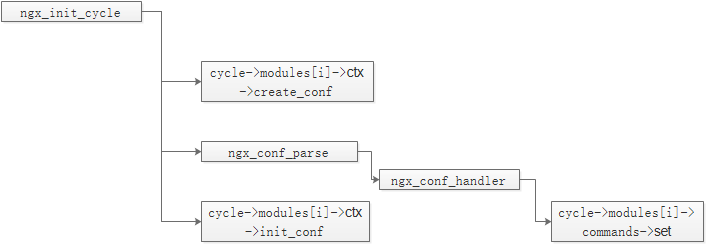
ngx_conf_parse是nginx提供的通用配置解析函数,ngx_conf_handler则将解析结果传递到其他模块进行处理。
nginx_conf_handler的部分代码如下:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last)
{
...
for (i = 0; cf->cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
cmd = cf->cycle->modules[i]->commands;
if (cmd == NULL) {
continue;
}
for ( /* void */ ; cmd->name.len; cmd++) {
if (name->len != cmd->name.len) {
continue;
}
if (ngx_strcmp(name->data, cmd->name.data) != 0) {
continue;
}
found = 1;
if (cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_CONF_MODULE
&& cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != cf->module_type)
{
continue;
}
/* is the directive's location right ? */
if (!(cmd->type & cf->cmd_type)) {
continue;
}
if (!(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_BLOCK) && last != NGX_OK) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"directive \"%s\" is not terminated by \";\"",
name->data);
return NGX_ERROR;
}
if ((cmd->type & NGX_CONF_BLOCK) && last != NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"directive \"%s\" has no opening \"{\"",
name->data);
return NGX_ERROR;
}
/* is the directive's argument count right ? */
if (!(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_ANY)) {
if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_FLAG) {
if (cf->args->nelts != 2) {
goto invalid;
}
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_1MORE) {
if (cf->args->nelts < 2) {
goto invalid;
}
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_2MORE) {
if (cf->args->nelts < 3) {
goto invalid;
}
} else if (cf->args->nelts > NGX_CONF_MAX_ARGS) {
goto invalid;
} else if (!(cmd->type & argument_number[cf->args->nelts - 1]))
{
goto invalid;
}
}
/* set up the directive's configuration context */
conf = NULL;
if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF) {
conf = ((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index];
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_MAIN_CONF) {
conf = &(((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index]);
} else if (cf->ctx) {
confp = *(void **) ((char *) cf->ctx + cmd->conf);
if (confp) {
conf = confp[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index];
}
}
rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf);
if (rv == NGX_CONF_OK) {
return NGX_OK;
}
if (rv == NGX_CONF_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"\"%s\" directive %s", name->data, rv);
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
...
}
各模块读取到配置存储在cycle结构体中:
struct ngx_cycle_s {
void ****conf_ctx; // 读取到的配置存在该变量中
...
ngx_module_t **modules;
ngx_uint_t modules_n;
...
}
conf_ctx 在内存中的布局如下:
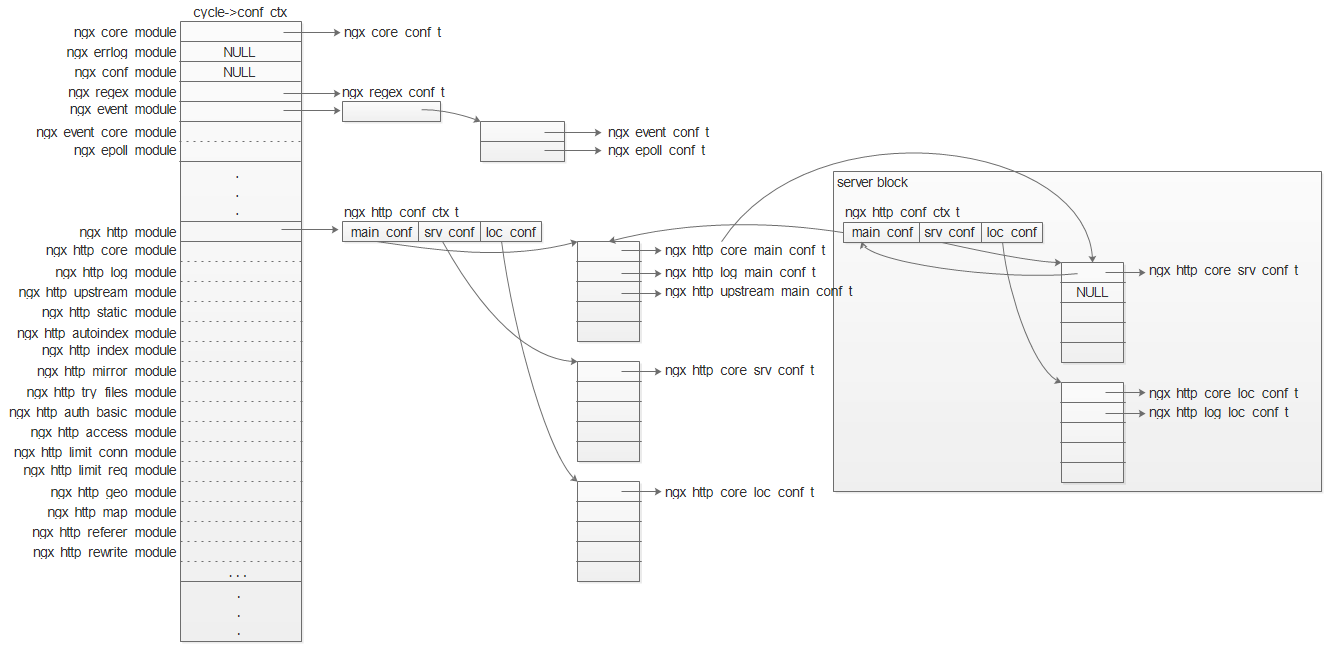
顶层模块的配置直接存储在conf_ctx中,二级模块的配置则存储在相应的顶层模块的配置区域所指向的区域。
顶层模块在接入二级模块时,需要帮二级模块分配空间按及读入配置,这个过程一般有固定的套路。
比如,对于ngx_event_module而言,它提供的配置解析命令如下:
static ngx_command_t ngx_events_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("events"),
NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_events_block,
0,
0,
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
这条命令表示解析nginx.conf文件中的events块,而用于解析events配置块的函数为ngx_events_block。
当我们编写nginx的扩展模块,需要解析我们自定义的配置块时,可以参考该函数:
static char *
ngx_events_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
char *rv;
void ***ctx;
ngx_uint_t i;
ngx_conf_t pcf;
ngx_event_module_t *m;
if (*(void **) conf) {
return "is duplicate";
}
/* count the number of the event modules and set up their indices */
ngx_event_max_module = ngx_count_modules(cf->cycle, NGX_EVENT_MODULE);
ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *));
if (ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, ngx_event_max_module * sizeof(void *));
if (*ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*(void **) conf = ctx;
for (i = 0; cf->cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
if (cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) {
continue;
}
m = cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx;
if (m->create_conf) {
(*ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index] =
m->create_conf(cf->cycle);
if ((*ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index] == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
}
}
pcf = *cf;
cf->ctx = ctx;
cf->module_type = NGX_EVENT_MODULE;
cf->cmd_type = NGX_EVENT_CONF;
rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL);
*cf = pcf;
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
return rv;
}
for (i = 0; cf->cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
if (cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) {
continue;
}
m = cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx;
if (m->init_conf) {
rv = m->init_conf(cf->cycle,
(*ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index]);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
return rv;
}
}
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
ngx_events_block的第三个参数conf来自于ngx_conf_handler的下面一段代码:
conf = NULL;
if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF) {
conf = ((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index];
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_MAIN_CONF) {
conf = &(((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index]);
} else if (cf->ctx) {
confp = *(void **) ((char *) cf->ctx + cmd->conf);
if (confp) {
conf = confp[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index];
}
}
rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf);
由于ngx_event_module的command type为:NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
所以,conf为:&(((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index])。
因为ngx_event_module是顶层模块,所以cf->ctx实际等于:cycle->conf_ctx,于是:
ngx_event_block传入的conf是:&(((void **) cycle->conf_ctx)[ngx_event_module.index])。
对于ngx_event_module,因为它是负责接入event二级模块的顶层模块,
所以它的配置区域不用来存储实际的配置,而是event二级模块配置的一个入口:
ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *));
if (ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, ngx_event_max_module * sizeof(void *));
if (*ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*(void **) conf = ctx;
上面的代码帮二级模块预分配好了配置存储空间,用的是通用指针。 各二级模块可能有各自不同的配置结构,需要自己创建:
for (i = 0; cf->cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
if (cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) {
continue;
}
m = cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx;
if (m->create_conf) {
(*ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index] =
m->create_conf(cf->cycle);
if ((*ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index] == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
}
}
比如,二级模块ngx_event_core_module的配置结构是:ngx_event_conf_t,它使用如下的函数创建该结构体:
static void *
ngx_event_core_create_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf;
ecf = ngx_palloc(cycle->pool, sizeof(ngx_event_conf_t));
if (ecf == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ecf->connections = NGX_CONF_UNSET_UINT;
ecf->use = NGX_CONF_UNSET_UINT;
ecf->multi_accept = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
ecf->accept_mutex = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
ecf->accept_mutex_delay = NGX_CONF_UNSET_MSEC;
ecf->name = (void *) NGX_CONF_UNSET;
return ecf;
}
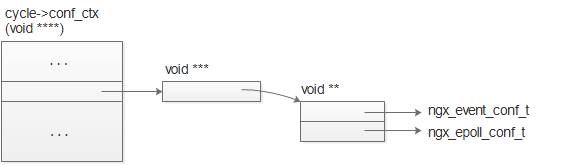
最终,ngx_event_module及其二级模块的配置在内存中布局方式如下:
«Previous: Linux工具汇总
»Next: nginx接入连接的过程